What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing within a business network. A blockchain database stores data in blocks that are linked together in a chain. The data is chronologically consistent because you cannot delete or modify the chain without consensus from the network. As a result, you can use blockchain technology to create an unalterable or immutable ledger for tracking orders, payments, accounts, and other transactions. The system has built-in mechanisms that prevent unauthorized transaction entries and create consistency in the shared view of these transactions.
Why is blockchain important?
Traditional database solutions pose various obstacles for capturing financial transactions. Consider the sale of a property. Once the money is exchanged, the buyer gains possession of the property. Individually, both the buyer and the seller can record monetary transactions, but neither source is reliable. The vendor can simply say they have not received the money when they have, and the buyer can also claim they have paid the money when they have not.
To avoid potential legal difficulties, transactions must be supervised and validated by a trustworthy third party. The presence of this central authority complicates the transaction and introduces a single point of risk. If the central database had been compromised, both parties could suffer.Blockchain addresses these difficulties by developing a decentralized, tamper-proof system for recording transactions. In the case of a property transaction, blockchain generates one ledger for each buyer and seller. All transactions must be approved by both parties and are automatically recorded in both ledgers in real time. Any corruption in historical transactions will affect the entire ledger. These qualities of blockchain technology have led to its application in a variety of industries, including the development of digital currencies like as Bitcoin.
How are blockchains used in various industries?
Blockchain is a new technology that is being implemented in novel ways by a variety of sectors. In the sections that follow, we describe some use examples in various industries:
Blockchain technology is used by energy companies to develop peer-to-peer trade platforms and facilitate renewable energy access. For instance, consider these applications:
Blockchain-based energy firms have developed a trading platform for the sale of electricity between individuals. This platform allows homeowners with solar panels to sell extra solar energy to their neighbors. The procedure is entirely automated: smart meters generate transactions, and blockchain records them.
Users can sponsor and own solar panels in underserved communities through blockchain-based crowd fundraising schemes. Sponsors may also get rent from these communities once the solar panels are constructed.
Finance
Traditional financial institutions, such as banks and stock exchanges, employ blockchain technology to manage online payments, accounts, and market trading. For example, Singapore Exchange Limited, an investment holding company that provides financial trading services throughout Asia, employs blockchain technology to create a more efficient interbank payment account. They overcame various hurdles by implementing blockchain, including batch processing and laborious reconciliation of thousands of financial transactions.
Media and Entertainment
Companies in the media and entertainment industries employ blockchain technology to manage copyright data. Copyright authentication is crucial for artists to receive fair compensation. It takes several transactions to document the sale or transfer of copyrighted content. Sony Music Entertainment Japan using blockchain technology to improve digital rights management efficiency. They have successfully implemented a blockchain strategy to increase efficiency and minimize costs in copyright handling.
Retail
Blockchain technology is used by retail companies to monitor items between suppliers and buyers. For example, Amazon Retail has filed a patent for a distributed ledger technology system that will employ blockchain technology to ensure that all goods sold on the platform are genuine. Amazon sellers can map their global supply chains by enabling participants like as manufacturers, couriers, distributors, end users, and secondary users to add events to the ledger after registering with a certificate authority.
What are the characteristics of blockchain technology?
The primary features of blockchain technology are as follows:
Decentralization
Decentralization in blockchain refers to the movement of control and decision-making from a centralized entity (person, company, or group) to a dispersed network. Decentralized blockchain networks employ transparency to eliminate the need for participants to trust one another. These networks also discourage users from exercising authority or control over one another in ways that undermine the network’s operation.
Immutability
Immutability indicates that something cannot be changed or altered. No one can tamper with a transaction once it has been recorded in the shared ledger. If there is an error in a transaction record, you must create a new transaction to correct the mistake, and both transactions are accessible to the network.
Consensus
A blockchain system creates criteria for obtaining participant approval before recording transactions. New transactions can only be recorded if the majority of network participants consent.
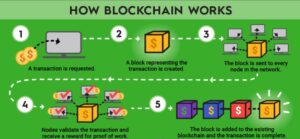
How does blockchain work?
While underlying blockchain mechanisms are complex, we give a brief overview in the following steps. Blockchain software can automate most of these steps:
Step 1 – Record the transaction
A blockchain transaction shows the movement of physical or digital assets from one party to another in the blockchain network. It is recorded as a data block and can include details like these:
Who was involved in the transaction?
What happened during the transaction?
When did the transaction occur?
Where did the transaction occur?
Why did the transaction occur?
How much of the asset was exchanged?
How many pre-conditions were met during the transaction?
Step 2 – Gain consensus
Most participants on the distributed blockchain network must agree that the recorded transaction is valid. Depending on the type of network, rules of agreement can vary but are typically established at the start of the network.
Step 3 – Link the blocks
Once the participants have reached a consensus, transactions on the blockchain are written into blocks equivalent to the pages of a ledger book. Along with the transactions, a cryptographic hash is also appended to the new block. The hash acts as a chain that links the blocks together. If the contents of the block are intentionally or unintentionally modified, the hash value changes, providing a way to detect data tampering.
Thus, the blocks and chains link securely, and you cannot edit them. Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and therefore the entire blockchain. This is like stacking wooden blocks to make a tower. You can only stack blocks on top, and if you remove a block from the middle of the tower, the whole tower breaks.
Step 4 – Share the ledger
The system distributes the latest copy of the central ledger to all participants.









